
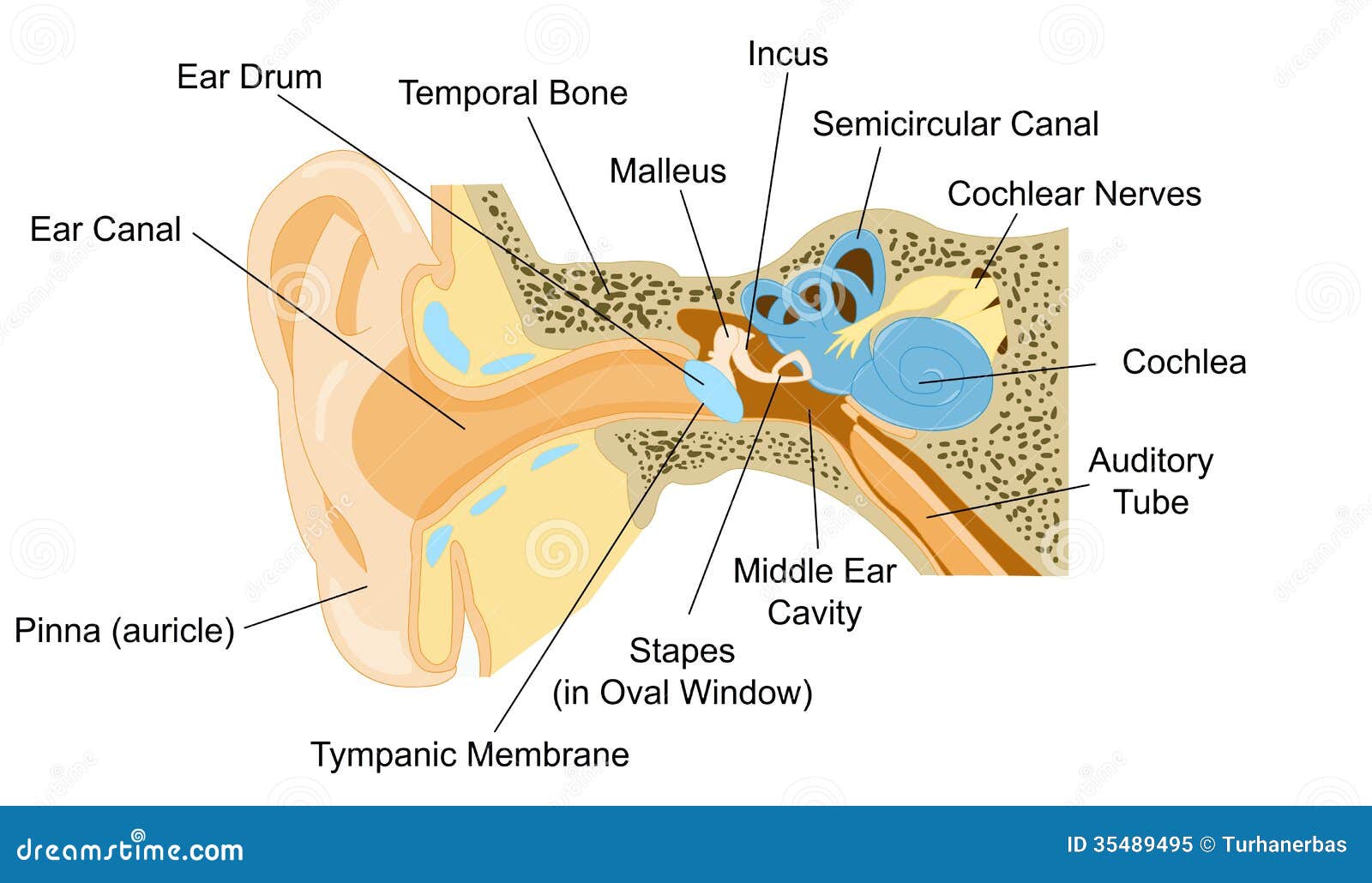

The special senses are served through the cranial nerves, as well as the general senses of the head and neck. The vagus nerve (cranial nerve X) has autonomic functions in the thoracic and superior abdominal cavities. The twelve cranial nerves serve the head and neck.

The cranial nerve exam allows directed tests of forebrain and brain stem structures. Finally, one nerve controls the muscles of the neck, assisting with spinal control of the movement of the head and neck. Four nerves make up the cranial component of the parasympathetic nervous system responsible for pupillary constriction, salivation, and the regulation of the organs of the thoracic and upper abdominal cavities. Four nerves connect to muscles of the face, oral cavity, and pharynx, controlling facial expressions, mastication, swallowing, and speech. Three nerves are connected to the extraocular muscles resulting in the control of gaze. Three of the nerves are strictly responsible for special senses whereas four others contain fibers for special and general senses. The nerves can be categorized by functions, and subtests of the cranial nerve exam can clarify these functional groupings. But knowing the names of the nerves in order often leaves much to be desired in understanding what the nerves do. The twelve cranial nerves are typically covered in introductory anatomy courses, and memorizing their names is facilitated by numerous mnemonics developed by students over the years of this practice.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
